Attentional Focus and Best Use of Self-Talk in Closed Skill Tasks
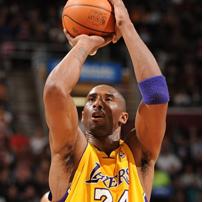
 International rugby stars and place kickers Dan Carter, Ronan O Gara and Jonny Wilkinson, among many others place the ball, set themselves, say something to themselves and mostly go about their business and put the ball between the posts.
International rugby stars and place kickers Dan Carter, Ronan O Gara and Jonny Wilkinson, among many others place the ball, set themselves, say something to themselves and mostly go about their business and put the ball between the posts.
So what exactly are they saying and why?
Research has shown that the use of psychological techniques can enhance sporting performance (Krane & Williams, 2006). Use of psychological techniques, cognitive strategies or mental training has been commonly used by high performance athletes for many years. Aided by the growth and development of sport psychology research in recent times, systematic cognitive strategies have become even more common-place as athletes seek out ways to improve performance and gain advantages over opponents. One mental strategy frequently used by athletes is self-talk (Hardy Oliver & Todd, 2009).
Self-talk has been shown to be beneficial for the learning of motor skills (Hardy, 2006). It can be defined as verbalization or statements athletes repeat to themselves prior to or during skill execution. These verbalization may be designed to affect motivation, attentional control, concentration and information processing. Landin (1994) suggested that the use of appropriate cue words may aid task focus by increasing focus on task relevant stimuli. Hardy (2006) suggests that the use of cue words may help athletes adjust their focus of attention towards a more appropriate attentional focus for completion of tasks.
Much empirical research has been carried out investigating the impact of such statements. Much of this has focused on motivational and instructional self talk. Motivational self talk tends to boost confidence and belief in one’s ability helping to raise performance while instructional tends to divert focus of attention on to certain elements of a movement to increase attentional focus and help task execution accordingly.
 Wulf et al’s attentional focus work draws a distinction between internal and external focus and shows that for skilled athletes, an external focus is better than an internal focus of attention. This may because an internal focus of attention draws attention towards little pieces of movement, thus reducing automaticity of that same movement.
Wulf et al’s attentional focus work draws a distinction between internal and external focus and shows that for skilled athletes, an external focus is better than an internal focus of attention. This may because an internal focus of attention draws attention towards little pieces of movement, thus reducing automaticity of that same movement.
Very little empirical research has differentiated between the different types of self-talk for skilled athletes in sporting tasks. Of such investigations, only power based motor tasks have been utilized. Both examples (Todd and McGuigan (2008) in a rugby power jump task & Goudas, Hatzidimitriou and Kikidi (2006) in a shot putt task) found that motivational self-talk was best.
Interestingly, no work has differentiated between the different types of self-talk for skilled athletes in closed skill tasks. That is until now.
New and yet unpublished research (Begley & Hardy) distinguishes that the most appropriate type of attentional focus will be dependent on the skill level of the performer. Using 40 inter-county level Gaelic Football free takers , this research investigated the differences between externally focused instructional self-talk (EFIST) and motivational self-talk (MST).
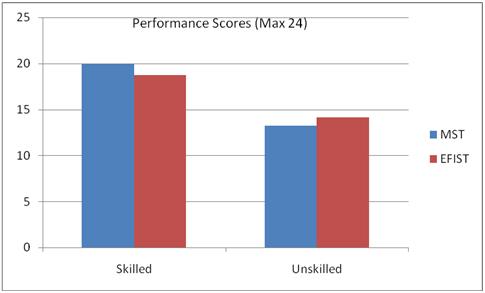
It is noteworthy that a two way ANOVA of data shows significant results favouring MST over EFIST in the skilled condition (see Fig.1). As this accuracy based study and all of the existing power based task research using skilled athletes (Edwards et al (2008) and Goudas et al, (2006)) replicate each other’s findings, it may be that motivational self-talk may exceed externally focused instructional self-talk in all tasks for skilled athletes by boosting athletes’ confidence and reinforcing belief in natural movement processes and well-honed skills.
 This will have ramifications for all sport psychologists working with elite level performers on closed skill tasks such as American football field goal, basketball free throw, rugby place kickers, dead ball specialists in soccer, GAA free takers, golfers, snooker and darts players.
This will have ramifications for all sport psychologists working with elite level performers on closed skill tasks such as American football field goal, basketball free throw, rugby place kickers, dead ball specialists in soccer, GAA free takers, golfers, snooker and darts players.
As it stands, certain psychologists, based on Wulf et al’s previous work have been guiding their athletes towards an external focus of attention. While it may augment what the athlete is already doing, it may not be the most effective way.
For more information, contact Elite Performance Sport Psychology at link below.
Elite Performance Sport Psychology Facebook Page
Keith Begley
MSc Applied Sport & Exercise Psychology.

























Hello dear Keith,
I am a full Ph.D student in motor behavior. I am interesting in your work that above mentioned (New and yet unpublished research (Begley & Hardy)because I am working on an issue that is like that.
I thank you send me this article or same articles.
best regards.